Blind signing in crypto is basically when you approve a transaction without being able to see all the details of what you’re actually signing. And, it’s risky because you could unknowingly give a malicious smart contract permission to drain your crypto wallet.
The truth is, blind signing is neither all good nor all bad, and it’s simply a tool that can open doors to DeFi apps, NFT markets, and more, but it also carries serious risks. In this guide, you’ll learn what blind signing really means, why it exists, and how to stay safe while using it.
“Blind signing” means approving a transaction you can’t fully read or verify (often shown as raw data or an unreadable blob). You’re trusting it without seeing what you’re agreeing to.
Authorizing a transaction where the details (token, amount, to/from, permissions) are hidden or unclear.
- Unknown or newly created contract addresses.
- Requests for token approvals you didn’t initiate.
- Promises of airdrops/refunds requiring a signature.
- Typosquatted URLs or fake social links.
- Read token, amount, to, and function (e.g.,
transfer,approve). - Prefer wallets that clearly decode calldata and highlight risks.
- Revoke old allowances regularly via a trusted token-approval checker.
Legit transactions are readable. If a wallet asks you to “blind sign,” treat it as a warning, not a shortcut.
What Is Crypto Blind Signing?
Blind Signing is you giving your digital signature to a transaction on a blockchain without being able to see all the details of that transaction. Well, you should think of it like this: you get a receipt at a store, but instead of seeing what you bought, it just says “Transaction Approved”. Next, you need to sign it anyway, no choice.
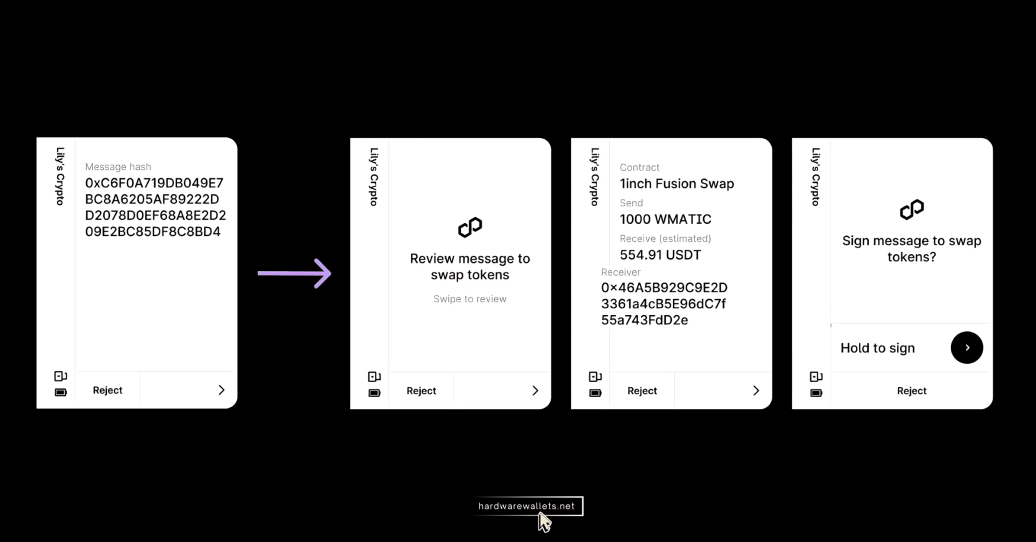
You know, a transaction is not just a number, but it’s a whole bunch of data. You’ve got the sender’s address, the recipient’s address, the amount of crypto, and maybe some other data bits if it’s a more complex transaction.
Your hardware wallet mainly shows you all of those details with a normal transaction. Basically, you look at the screen, you check that everything looks right, and then you press the button to approve.
Now, with blind signing, some of that information is hidden from you. You might see the amount and who you’re sending it to, but other parts of the data, especially what’s called the “smart contract data,” are just gibberish.
You’re actually saying, “Yeah, I trust this,” and you just go for it, even though you can’t verify everything.
In 2020, the founder of Nexus Mutual, Hugh Karp, lost around $8M after an attacker gained remote access to his computer and modified the MetaMask extension. Hugh was using a hardware wallet, yet he still approved a transaction that sent funds to a thief. Well, it wasn’t the device that failed him; it was blind signing.
So, why does it exist?
Blind signing exists all the time for a few important reasons:
- Smart contracts are complex: DeFi platforms, yield farms, and NFT marketplaces all run on contracts with multiple functions. Actually, your wallet might not be able to display every detail, so you see a hash or a vague “Data present” message instead of a clear summary.
- Hardware wallets have small screens: You should know one thing about hardware wallets, as secure as they are, those tiny OLED screens aren’t meant for reading long text. They connect to companion apps like MetaMask or Ledger Live, and if the app can’t interpret the contract, you’re basically stuck with a bunch of gibberish. And you need to sign it, you’ve got no choice. That’s how this works, and it’s completely normal.
- Privacy features sometimes require it: Sometimes, certain privacy‑focused protocols intentionally hide parts of a transaction from the signer to preserve anonymity. Well, that’s technically clever, but it adds another layer of confusion.
Debunking myths and misconceptions
Over the years, I’ve heard a lot of myths about blind signing. Let me address a few:
“My hardware wallet makes me invincible.” Not quite. Yes, it protects your private keys, but if you blindly approve a transaction, the hardware won’t magically know it’s a scam. Actually, the device does what you tell it to do.
“Only DeFi pros need to worry about blind signing.” Wrong again. Even simple NFT purchases or token transfers can involve contracts your wallet doesn’t understand. So, beginners face the same risks.
“If the site is popular, it’s safe.” Scammers clone websites and mimic user interfaces. I’ve seen phishing sites that look identical to Uniswap or OpenSea. Hence, if you blindly sign up on those sites, you’re done.
“Blind signing is always bad.” Well, it’s risky, but it has legitimate uses in privacy protocols and advanced financial tools. The best trick is to know when it’s necessary and how to protect yourself.
What Kind of Transactions Need Blindly Signing?
Generally, blind signing is needed for transactions that involve something other than just sending a specific amount of crypto from one wallet to another.
Mainly, blind signing is needed for these types of actions:
- Interacting with Smart Contracts: This is the most common reason, as smart contracts are basically just computer programs on the blockchain. You have to sign in to interact with them, but your hardware wallet might not be able to translate all of the code to plain English. So, you are just signing a contract you can’t read.
- Staking and DeFi: When you put your crypto into a DeFi protocol to earn interest, you are interacting with a smart contract. Again, that transaction might require blind signing.
- NFTs: Buying, selling, or “minting” NFTs all involve smart contracts. Hence, a lot of times, you’re not just sending crypto, you are also signing an agreement for the unlimited token use.
- Decentralized Apps (dApps): Here also, using any dApp, whether it’s for trading, gaming, or whatever, will involve smart contracts. Hence, your wallet will likely ask you to blind sign.
Is Blind Signing really that bad (I don’t think)
I guess the short answer is: yes and no.
It is really bad because it exposes you to serious risks. Honestly, if you don’t know what you’re doing, you should probably avoid it. Look at all the stories of people who lost their money, and that’s enough reason to be super careful.
But, at the same time, blind signing is kind of a necessary evil. Right now, there isn’t a better way for hardware wallets to show you all the complex details of every single transaction. It’s a temporary solution to a technology problem. Eventually, we’ll see better wallets and better technology that let you see exactly what you’re signing.
Until then, you just have to be smart about it. Blind signing is not always bad. It is only bad when you do it without being careful.
A “What You See Is What You Sign” Is What You Really Want
Exactly. What you really want is the opposite of blind signing, also called clear signing. It’s a type of transaction where your hardware wallet can show you all the details in a way you understand.

So, your cryptocurrency wallet will literally say, “You are sending 10 ETH from address A to address B.” This is what’s called a “What You See Is What You Sign” (WYSIWYS) transaction.
Today, this is the gold standard for security, and it also means there’s no way for a hacker to hide a malicious command inside the transaction. You can double-check everything before you approve it.
Blind Signing vs. Clear Signing
| Criteria | Blind Signing | Clear Signing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Signs a transaction without seeing the full details. | Full visibility into all details |
| Transparency | Low. The signer cannot review what is being signed | High. You can easily read and confirm all information |
| Security Risk | Very risky. Malicious instructions can be hidden | Safer. Risks are reduced since details are visible |
| User Control | Limited | Strong |
| Typical Use Cases | Privacy protocols, zero-knowledge proofs, confidential transactions. | Everyday wallet transactions, contracts, digital document signing |
| Trust Requirement | Requires heavy trust in the application or protocol | Trust is based mainly on the signer’s own review |
| User Experience | Quick and simple but dangerous | Slightly slower but much safer |
| Attack Surface | High. Attractive for phishing and hidden exploits | Lower. Attacks are harder when details are exposed |
| Best Practices | Should be avoided except for very specific privacy needs | Recommended as the default for wallets and applications |
How to Avoid Blind Signing Signature Scheme?
You can totally protect yourself from blind signing scams. To do so, you just need to follow some basic rules. They’re not hard at all, just a few things to remember.
1. Know Your Hardware Wallet
You need to learn how your wallet works. Some crypto wallets, like Ledger, have a feature that mainly lets you turn off blind signing for certain coins. So, it’s probably a good idea to do this, and that way, you’ll never accidentally sign a bad transaction.
Also, always read the screen and look at what your wallet is telling you. If it says “Review transaction” but the details on the screen don’t make sense, or it says something like “Blind signing enabled,” you should probably not sign.
2. Be Careful with Websites and dApps
Today, there are a lot of scammers creating fake websites that look just like the real ones. Mainly, they will use a fake URL with a few letters changed. So, always double-check the URL before you connect your wallet.
Never connect to a website you don’t trust, and if a social media friend sends you a link to a new airdrop or a new app, don’t just click it. Also, you should totally disconnect your wallet when you are done using a dApp. A lot of people forget to do this, and it makes them more of a target.
3. Use a Separate Wallet for dApps
This is a really smart tip…
You can have one wallet for your main crypto savings (your “cold storage” wallet) and another wallet for interacting with dApps (your “hot wallet”). You just have to move a small amount of crypto to the hot wallet when you need to use a dApp.
That way, even if you do blind sign something bad, you can only lose a small amount of money, actually.
4. Learn
Finally, learn about the things you are doing, and don’t just follow a tutorial without knowing what you’re doing. You have to take some time to understand what a smart contract is, what an ETH transaction looks like, and what your wallet’s screen is actually telling you.
Which Hardware Wallets Support Blind Signing or Clear Signing
- Ledger wallets (Nano X, Flex, etc.) are the only ones with documented support for both
- ELLIPAL Titan 2.0 and Keystone 3 Pro stand out in the hardware wallet category with a big 4-inch screen and contract-address labeling. Both support clear signing.
- Software wallets (MetaMask, Trust Wallet, etc.) generally rely on blind signing and have no secure, tamper-proof display, making them more vulnerable and lacking any clear signing feature.
| Wallet | Blind Signing | Clear Signing |
|---|---|---|
| Ledger Nano X | Supported when needed (especially outside Ledger Live integrations); prompt appears | Supported within Ledger Live integrations (“clear signing” initiative) |
| Ledger Flex | Same as other Ledger devices (i.e., supported when needed) | Same support via Ledger Live integrations |
| Trezor Safe 3 & 5 | Yes | No |
| ELLIPAL Titan 2.0 | Yes | Yes |
| Keystone 3 Pro | Yes | Yes |
| SafePal | Yes | No |
| BitBox | Yes | No |
| KeepKey | Yes | No |
The Future of Blind Signing
Honestly, I guess the long-term solution is to get rid of blind signing completely. It’s not a great way to do things, and it puts people at risk. Well, the good news is that people are working on this, and even developers are making new wallets and new software that are better at translating smart contract data into something you can understand.
Eventually, we’ll probably have a world where you never have to blind sign a transaction again. So, every transaction, even the really complicated ones, will be readable on your hardware wallet’s screen. That’s the dream, anyway.
So, in the end, blind signing is just a reality of using crypto right now. Again, it can be a huge risk, but if you’re smart and you take the right steps, you can avoid a lot of the danger. You have the power to protect your crypto, but you just need to be a little bit more careful than you normally would.
Is crypto blind signing a scam?
No, blind signing itself is not a scam, but it is actually a major security risk that scammers totally exploit. Also, it is a necessary part of some crypto transactions, especially for features like DeFi and NFTs.
But, because you cannot see the full details, a hacker can easily trick you into approving a bad transaction. A lot of people have lost their money this way.
What is blind signing on Ledger?
Blind signing on Ledger means approving a transaction without the device showing complete details. Ledger devices sometimes cannot decode smart contract data, so they display only a generic “Data present” message.
In that case, you must choose whether to confirm without knowing the full picture. Also, Ledger supports clear signing when possible, but blind signing remains a fallback for certain dApps and tokens that the interface cannot fully interpret.
Why is blind signing important?
Blind signing is important because it allows interaction with many decentralized apps that otherwise wouldn’t work. As discussed above, complex DeFi, NFT platforms, and certain privacy protocols often require it.
Hence, you may be locked out of large parts of Web3 without blind signing. At the same time, it’s a double-edged sword since you could be confirming harmful transactions. So, knowing when and how to use it safely makes the difference between opportunity and loss.
You can also read my guides on the best hardware wallets and best cold crypto wallets…
